|
| February 14, 2010: Viktor Yanukovych wins the Ukrainian presidential election, overturning the so-called Orange Revolution, and changing the balance of power in Eastern Europe.. |
By F. William Engdahl
March 22, 2010
http://oilgeopolitics.net
Images and captions added by the editors
Part I: The Geopolitical significance of Ukraine today
A decisive vote against NATO
On February 14 Ukraine's Election Commission declared Viktor Yanukovych the winner in that embattled country's Presidential runoff vote, defeating former Prime Minister and Orange Revolution instigator Yulia Tymoshenko. Contrary to the positive spin Washington is trying to put on the events, they mark the definitive death of Ukraine's much-touted “Orange Revolution.“
The relevant question at this juncture is what the defeat of Ukraine's Orange Revolution signifies for the future of the Eurasian Heartland, as British geopolitician Halford Mackinder termed the region? Even more significantly, what does it imply for a two-decade long Pentagon attempt to weaken and ultimately cripple Russia as a military power in Washington's awesome and overly-ambitious agenda of Full Spectrum Dominance?
To understand the long-term significance of the Ukraine vote for the future global geopolitical balance of power we should go back to the original Orange Revolution of 2004. Viktor Yushchenko was the hand-picked candidate of Washington, and especially the neo-conservatives around the Bush Administration, in their attempt to split Ukraine from its historic and economic ties to Russia and bring the country, along with neighbor Georgia, into NATO.
Ukrainian economic and political geography
A look at the map will indicate just how strategic Ukraine is for both NATO and for Russia. Not only does the country directly border Russia to its east, but it also provides the transit route for most Russian natural gas pipelines to western Europe -- some 80% of all Russian gas exports from which the country earns dollars, a vital economic lifeline for Russia.
Perhaps equally vital for Russia, in terms of her ability to maintain a credible defense against ever-growing NATO encirclement of its land area, is the Russian leasing rights to Ukraine's Black Sea port of Sevastopol, home to Russia's Black Sea Naval Fleet. The Fleet leases an additional home port in Odessa, in an agreement between Russia and Ukraine. This politically sensitive bilateral treaty for the Black Sea Fleet basing is not due to expire until 2017, if not renewed. Following the Russia-Georgia conflict in August 2008, Ukraine’s President Yushchenko began making noises about prematurely terminating that treaty, thereby depriving Moscow of its strategically most important naval base. Russian navy ships have used Sevastopol since Russia annexed the region in 1783.
The eastern part of Ukraine bordering Russia is home to more than 15 million ethnic Russians and remains literally the bread basket of eastern Europe, with some of the richest soil on earth. In 2009 Ukraine was the world's third largest grain exporter after the USA and EU, and ahead of Russia and Canada.[1] Ukraine's famous black soil, chornozem, is considered the most fertile in the world, and covers two-thirds of Ukraine.[2] The area around the rivers Dnieper and Dniester is the only place in the world where the width of the so-called ‘sweet’ black soil reaches 500 km. This soil is exceptional in providing very high quality harvests and belongs to the national wealth. Western agribusiness companies such as Monsanto, Cargill, ADM and Kraft Foods are reportedly salivating over the prospect of an end to the internal Ukrainian political stalemate in hopes of exploiting these resources. [3]
The Ukrainian Donetsk region in the eastern Donets Basin or Donbas is the political base of newly elected President Yanukovych. It is the most populous region of Ukraine and the center of its coal, steel and metallurgy industries, science centers and universities. Ukraine's Donbas contains an estimated 109 billion tons of coal as well as oil and gas.
Overall, Ukraine is one of the richest regions in all Europe for natural resources including granite, graphite, and salts. It provides a rich source for metallurgical, porcelain, chemical industries, for production of ceramics and building materials. [4]
In short, capture of the Ukraine in 2004 was a prize of strategic geopolitical importance for Washington in its bid for what the Pentagon terms ‘Full Spectrum Dominance’—control of the entire planet: land, air, oceans, space and outerspace. As the British father of geopolitics, Sir Halford Mackinder wrote in his seminal 1919 book, Democratic Ideals and Reality,
Who rules East Europe commands the Heartland:
Who rules the Heartland commands the World-Island:
Who rules the World-Island commands the World.5
 |
| Mackinder's Heartland |
Yushchenko almost succeeded but for the ill-conceived adventure of Georgia's hand-picked Rose Revolution President, Mikhail Saakashvili in August 2008, sending troops to reclaim the seccessionist region of South Ossetia and Abkhazia for Georgia just weeks before NATO ministers would vote on Ukrainian and Georgian NATO membership. The swift Russian military response in stopping the Georgian attack and routing Saakashvili's rag-tag forces also stopped dead any chance that Germany or other NATO countries would OK NATO membership, and with it the pledge to come to the defense of either Georgia or Ukraine in a war against Russia. [6]
Significance of the Orange Revolution
The "revolution" that swept Viktor Yushchenko into power on a wave of US dollars and support from US-backed NGO's, was initially conceived at the Washington-financed RAND corporation. RAND had studied the swarming pattern of bees and similar phenomena, and applied these to modern mobile communication, text messaging and civil protest as tactics for regime change and covert warfare. [7]
As I describe in some detail in my book, Full Spectrum Dominance: Totalitarian Democracy in the New World Order, the transformation of Ukraine from independent former Russian republic to a pro-NATO US satellite was accomplished by the so-called ‘Orange Revolution’ in 2004. It was overseen by John Herbst, appointed US Ambassador to Ukraine in May 2003, just months before the events were set off. As the US State Department euphemistically described his activities:
During his tenure, he worked to enhance US-Ukrainian relations and to help ensure the conduct of a fair Ukrainian presidential election. In Kiev, he witnessed the Orange Revolution. Prior to that, Ambassador John Herbst was the US Ambassador to Uzbekistan, where he played a critical role in the establishment of an American base to help conduct Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan.[8]
John Herbst
The man Washington decided to back in its orchestrated regime change in Ukraine was Viktor Yushchenko, a fifty-year old former Governor of Ukraine’s Central Bank who had been the point man in Ukraine for the savage IMF "shock therapy" deindustrialization of the country during the 1990's. Yushchenko's IMF program had devastating consequences for his countrymen. Under his 1994 IMF program, Ukraine was forced to abandon exchange controls and let the currency fall. He oversaw the currency demands as head of the central bank, which within days saw the price of bread increase by 300%, electricity prices by 600%, public transportation by 900%. By 1998 Ukrainian real wages had fallen by 75% compared with 1991 when the country declared independence. He was clearly Washington's man for what they wanted to do in Ukraine. [9]
Yushchenko’s wife Kateryna, an American citizen born in Chicago, had been an official in both the Reagan and George H.W. Bush administrations, and in the US State Department. She had come to Ukraine as a representative of the US-Ukraine Foundation whose Board of Directors included Grover Norquist, one of the most influential conservative Republicans in Washington. Norquist had been called ‘the managing director of the hard-core right,and was a key political figure behind the consolidation of right-wing organizations in support of the George W. Bush Presidency. [10]
 |
| Viktor & Kateryna Yushchenko |
In Ukraine the pro-Yushchenko movement worked under the slogan Pora (‘It's Time’) and they brought in people who had helped organize the ‘Rose Revolution’ in Georgia: Chair of Georgia’s Parliamentary Committee on Defense and Security, Givi Targamadze; former member of the Georgian Liberty Institute; and Georgia’s youth group, Kmara. The Ukrainian opposition leaders consulted the Georgians on techniques of non-violent struggle. Georgian rock bands Zumba, Soft Eject and Green Room, which had supported the ‘Rose Revolution,’ now organized a solidarity concert in Kiev to support Yushchenko’s 2004 campaign.[11]
A Washington-based PR firm called Rock Creek Creative also played a significant role in branding the Orange Revolution by developing a pro-Yushchenko website around the orange logo and its carefully-staged color theme. [12]
When Yushchenko lost the 2004 election to Viktor Yanukovych, several elements worked in concert to create an aura of fraud around the results, and to mobilize popular support for a new run-off. Using the Pora and other youth groups, especially election monitors, in coordination with key western media such as CNN and BBC, a second election was organized that allowed Yushchenko to squeak out a narrow margin of victory in January 2005 and declare himself President. The US State Department reportedly spent some $20 million to secure a US-friendly outcome in the Ukraine Presidency. [13]
The same US Government-backed NGOs that had been in Georgia produced the results in Ukraine: the George Soros’ Open Society Institute, Freedom House (whose head at the time was former CIA Director James Woolsey), the National Endowment for Democracy and its subsidiaries, the National Republican Institute and the National Democratic Institute. According to Ukrainian reports, the US-based NGOs, along with the conservative US-Ukraine Foundation, were active across Ukraine, feeding the protest movement of Pora and Znayu, and training the crucial poll watchers.[14]
President Viktor Yushchenko, Washington's man in Kiev, moved immediately to disrupt economic links to Russia, including shutting off Russian natural gas into western Europe via Ukrainian transit pipelines. This move was used by Washington to try to convince EU countries, especially Germany, that Russia was an "unreliable partner." Some 80% of Russia's gas was exported via Ukrainian pipelines that had been built during the Soviet Union era when the two countries were one economic and political entity.[15] Yushchenko also worked closely with US-backed President Mikhail Saakashvili, Washington's man in neighboring Georgia.
The final result of the 2010 Ukrainian elections was an overwhelming rejection by voters of Yushchenko, the “hero” of the Orange Revolution, who received barely 5% of the vote. After five years of economic and political chaos, Ukrainians clearly want some kind of stability. Opinion polls in Ukraine show a majority opposed to joining NATO.
Western media depictions of incoming Ukrainian President Viktor Yanukovych as some kind of Moscow puppet, however, appear wide of the mark; his major industrial backers want harmonious economic relations with the European Union as well as with Russia.
Yanukovych announced that his first official trip abroad will not be to Moscow but rather to Brussels to meet with leading EU officials. After that, he will immediately fly to Moscow, where President Medvedev has signaled anticipation of improved cooperation by re-instating Russia’s Ambassador to Kiev after months of political tensions between Yushchenko and Moscow had put the appointment on hold.
Most significantly, however, and contrary to his predecessor’s relentless attempts to pull Ukraine into NATO on Washington’s urgings, Yanukovych announced he would not meet with NATO officials in Brussels. In interviews with Ukrainian media, Yanukovych has clearly stated that he will not try to bring Ukraine into either the EU or, most importantly for Moscow, into NATO.
Yanukovych has pledged to focus instead on Ukraine’s economic crisis and political corruption. Regarding Moscow, he has added that he will welcome Russia into a consortium that would jointly operate Ukraine's natural gas pipeline network, restoring influence that Yushchenko and his highly ambitious Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko tried to cancel. Another important signal not welcomed in NATO circles was his announcement that he would extend Russia's strategically vital lease on the naval base at the Ukrainian port of Sevastopol due to expire in 2017. [16]
Russia’s new Geopolitical Calculus
It’s clear that Yanukovych’s bitter election opponent, Orange Revolution veteran and former Prime Minister Yulia Tymoshenko, has bitterly opposed Yanukovych’s policy, at the very least because she is fighting for her political ambitions and is known to be a sore loser. After her challenge to the February election results failed in Ukrainian courts, she announced she would use her parliamentary coalition to block Yanukovych. Under normal procedures, she should have resigned as Prime Minister after the Yanukovych victory (by a margin of one million votes) was certified, as President-elect Yanukovych asked on February 10. She refused. She was supported as the preferred Presidential candidate by Germany’s Angela Merkel and other EU leaders. [17]
 |
| Rinat Akhnetov |
The Ukrainian Parliament delivered a vote of no confidence on March 3 against the sitting government of Prime Minister Tymoshenko, by a majority of 243 out of 450. This was the death knell for Tymoshenko’s faction of the 2004 Orange Revolution and it opens up the possibility of finally breaking a political stalemate among Ukraine’s political factions that has existed since shortly after the 2004 Orange Revolution. The ball is now clearly in Yanukovych’s court. [18]
In the late 1990’s before she co-led the Orange Revolution, Yulia Tymoshenko was president of Ukraine’s United Energy Systems, a privately-owned importer of Russian natural gas into Ukraine. She was accused by Moscow of illegally reselling enormous quantities of stolen Russian gas and avoiding tax on the sales during the late 1990s, whence she got the nickname in Ukraine as “gas princess.”
 |
| "Gas princess" (and former prime minister) Yulia Tymoshenko |
Assuming that Yanukovych is now able to proceed with stabilizing the country along the neutral lines noted following the defeat of the Tymoshenko government, Moscow gains a major shift in the political tectonic plates that comprise the Eurasian Heartland, even with a strictly neutral Ukraine.
First, the strategic military encirclement of Russia -- via NATO’s attempted recruitment of Ukraine and Georgia -- is now clearly blocked and off the table. Russia’s access to the Black Sea via Ukraine’s Crimea appears assured as well.
 |
| Pre-2010 NATO expansion map. Ukraine no longer seeks membership. |
This altered geopolitical configuration in central Eurasia after the defeat of the Orange Revolution gives a strong boost now to Russia’s long-term energy strategy—a strategy that we might call Russia’s North-South-East-West Strategy.
Part II: Russia’s New Geopolitical Energy Calculus
Russia’s North-South-East-West energy strategy
The defusing of major Washington military threats is far from the only gain for Moscow in having a neutral but stable Ukrainian neighbor. Russia now vastly improves its ability to expand the one great power lever it has, outside of its remaining and still formidable nuclear strike force. That lever is to counter Washington’s relentless military pressure by cleverly using export of the world’s largest reserves of natural gas, a fuel much in demand in Western Europe and even in UK where North Sea fields are in decline.
According to west European industry estimates, demand within the European Union countries for natural gas, especially for use in electric power generation where it is seen as a clean and very efficient fuel, is estimated to rise some 40% from today’s levels over the next twenty years. That increase in gas demand will coincide with a decline in current gas output from fields in the UK, Netherlands and elsewhere in the EU. With Ukraine’s shift from hostile opposition to Moscow to what Yanukovych terms ‘non-aligned’ neutrality -- with an early emphasis on stabilizing Russian-Ukrainian gas geopolitics -- Moscow suddenly holds a far stronger array of economic options with which to neutralize Washington’s game of military and economic encirclement.
When Yushchenko and Georgia's Saakashvili took the reins of power in their respective countries and began taking steps with Washington to join NATO, one of the few means available for Putin’s Russia to re-establish some semblance of economic security was its energy card. Russia has by far the world's largest known reserves of natural gas. Interestingly, according to US Department of Energy estimates, the second largest gas reserves are in Iran, a country also high on Washington's target list.
 |
| Russian President Medvedev, former head of Gazprom |
High-stakes Eurasian chess game
In a sense, the Eurasian land area today resembles a geopolitical game of three-dimensional chess between Russia, the European Union member countries, and Washington. The stakes of the game are a matter of life and death for Russia as a functioning nation, something clearly Medvedev and Putin well realize at this point.
US attempts at the military encirclement of Russia included not only the Rose and Orange Revolutions in 2003 and 2004, but also the highly provocative Pentagon missile ‘defense’ policy of placing US-controlled (not NATO-controlled) missiles in key former Warsaw Pact countries on Russia’s direct perimeter. As a result, Moscow has developed a remarkable and complex energy pipeline strategy to undercut a clearly hostile US military strategy that has used NATO encirclement, missile deployments, and ‘color revolutions,’ including the attempted destabilization of Iran during summer 2009 with a ‘Green Revolution’ or what Hillary Clinton flippantly dubbed the ‘Twitter Revolution.’ All of these US moves have attempted to isolate Russia and weaken her potential strategic allies across Eurasia.
For Russia, which recently surpassed Saudi Arabia as the world’s largest oil producer and exporter, sales of its natural gas abroad has a significant advantage in that Moscow is better able to control the price and market of gas. Unlike oil, whose price is tightly controlled by a cartel of Big Oil (and their Wall Street co-conspirators such as Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, JP Morgan Chase), natural gas is far more difficult for Wall Street to manipulate on a short-term speculative basis as with oil.
Because gas, unlike oil, is dependent on construction of costly pipelines or LNG tankers and LNG port terminals, it tends to have a price fixed by bilateral long-term agreements between buyer and seller. That gives Moscow a degree of protection against events such as the brazen Wall Street manipulation of oil prices in 2008-2009 from a record high of $147 a barrel down to below $30 only months later, manipulations which devastated Moscow’s oil earnings at just the time the global financial crisis cut off credit to Russian banks and companies.
With Yanukovych now President in Ukraine, the way appears clear for a rational gas supply and transit contract from Russia’s Gazprom to and through Ukraine, and continuing on to western Europe. Fully half of Ukraine’s domestic energy comes from natural gas and the overwhelming bulk of that gas, some 75%, comes from Russia.
At this point it seems a stable settlement has been reached between the Russian and Ukrainian governments on pricing for imported Russian gas. As of January 2010 Ukraine has agreed to pay prices close to western European levels for its gas, and at the same time she will get significantly higher transit fees from Russia’s state-owned Gazprom for transporting Russian gas through to western Europe. Some 80% of Russian gas exports went through Ukraine up until now.
That’s about to change dramatically however, with the implementation of Russia’s long-term pipeline strategy, a strategy designed to make Russia less vulnerable to future political shifts such as the 2004 Ukraine Orange Revolution.
After the 2004 Ukraine Orange Revolution, Moscow’s western pipeline strategy until now has been to bypass both Ukraine and Poland through construction of an underwater gas pipeline, Nord Stream, running from Russia directly to Germany. Poland’s Foreign Minister Radek Sikorski is a Washington trained neo-conservative . As the previous Defense Minister, he played a central role in Poland’s missile defense agreement with Washington. Sikorski’s Poland today is bound closely to NATO, including agreeing to Washington’s militarily provocative missile deployment policies, and he is trying at every turn, so far unsuccessfully, to block construction of Nord Stream.
 |
| Nord Stream pipeline, scheduled to become operational in October, 2011 |
 |
| Click to enlarge |
Sikorski’s logic was not so precise but his emotional imagery was.
In late 2009 Sweden and Finland joined Denmark in finally granting passage rights through their portion of the Baltic Sea for the pipeline. Construction of the multi-billion dollar project is due to begin this April and gas deliveries are to begin in 2011. When a second parallel pipeline, due to start construction in 2011, is completed, Nord Stream anticipates a full capacity of 55 billion cubic meters of gas a year, enough to fuel 25 million households in Europe, according to the Nord Stream website.
 |
| Building Nord Stream |
At the end of 2009 in Minsk, just as Nord Stream was clearing the final political hurdles, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev met with Belarus officials. Medvedev said that Russia was considering a second leg of its large Yamal-Europe gas pipeline through Belarus if future demand from western Europe warranted, stating, “I think the more possibilities there are for Russian gas supplies to Europe, the better it will be for both Europe and Russia.”
In addition, in a notable geopolitical shift, the UK has just signed a long-term contract with Gazprom to import gas via the Nord Stream to meet more than 4% of UK gas demand by 2012, as Britain shifts from being a gas exporter to a gas importer. Presently, in addition to the UK and Germany, Gazprom now has contracts to supply Denmark, The Netherlands, Belgium and France, making it a major new factor on the EU energy supply market.
The Russia-Turkey South Stream Pipeline Strategy
Meanwhile, Washington, bitterly opposed to Nord Stream, attempted unsuccessfully to block it by proxy through back-door support for Poland and other EU opposition.
In a second major front in what could be called the Russia-USA pipeline wars, the US has initiated competing proposals to build gas pipelines to serve the countries of southern and southeastern Europe. Here Washington is openly backing what is called the Nabucco pipeline project. Moscow is promoting what it calls its South Stream project, the southern Eurasian sister to the Nord Stream in the north of Europe.
On December 12, 2009 the government of Bulgaria, a former Warsaw Pact member now in NATO and the EU, announced that it would participate in Moscow’s South Stream project despite considerable pressure from Washington.
 |
| South Stream pipeline project, exact route yet to be determined, currently scheduled for completion in 2015 |
South Stream’s offshore section is to run under the Black Sea from the Russian coast to the Bulgarian coast, a length of around 550 miles at a maximum depth over two kilometers and have a full capacity of 63 billion cubic meters, even larger than Nord Stream.
From Bulgaria, South Stream will split into two arms, the northern section stretching to Romania, Hungary, the Czech Republic and Austria and the southern arm going through Bulgaria to southern Italy. The new pipeline is expected to become operational in 2013.
Gazprom has an agreement to provide Italy with gas until 2035 and South Stream will be the main vehicle for that. South Stream AG, the 50-50 Gazprom-ENI joint venture is registered in Switzerland. To date Gazprom has signed transit agreements for the pipeline with the Republic of Serbia and Greece and Hungary. In January 2008, Gazprom bought 51% of the Serbian state oil monopoly NIS to secure its presence there.
An indication of the pressure that Washington has put on Bulgaria over its participation in Russia’s South Stream is that Bulgaria also signed up to take part in the Nabucco project in December 2009. Commenting on the dual signings, Bulgaria’s Prime Minister Boyko Borisov told the press, “Nabucco is a priority of the European Union while the Russian South Stream is moving forward very quickly and many European countries are joining it almost daily.”
On March 3, 2010 the new Croatian government of Prime Minister Jadranka Kosor signed an agreement in Moscow with Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin allowing the pipeline to pass through Croatian territory, setting up a 50-50 joint venture to realize the construction.
Kosor said that the agreement ‘On the Construction and Exploitation of a Gas Pipeline on Croatian Territory’ creates a legal basis for Croatia's involvement in South Stream, allowing the parties to set up a 50/50 joint venture. Two days later, in what seemed a snowballing enthusiasm for Gazprom’s project, the Bosnian Serb Republic announced that it, too, will join the South Stream gas pipeline project. It proposes to build a 480 km pipeline in northern Bosnia and link it to the South Stream pipeline, bringing the total number of participating countries that have signed deals with Gazprom to seven.
In addition to Serb Bosnia, Gazprom’s partners now include Bulgaria, Hungary, Greece, Serbia, Croatia and Slovenia. It almost retraces the Balkan route of the controversial Berlin-to-Baghdad railway that played such a decisive geopolitical role in British machinations that ultimately led to World War I following the assassination of the Austro-Hungarian heir to the throne, Archduke Francis Ferdinand.
The central issue for the two competing pipeline projects, South Stream and Nabucco, is not who will buy their gas. As noted, natural gas demand across Europe is expected to rise dramatically in coming years. Rather it’s the question of where the gas will come from to fill the pipeline. Here Moscow now clearly holds the trump cards.
In addition to gas directly from Russia’s gas fields, a major component of South Stream gas is to come from Turkmenistan and from Azerbaijan and possibly at some point from Iran. In December 2009 Russian President Dmitry Medvedev went to Turkmenistan to sign major agreements on energy cooperation.
Until the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, Turkmenistan was a republic of the Soviet Union, the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, Turkmen SSR. It is bordered by Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest, Uzbekistan to the east and northeast, Kazakhstan to the north and northwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Russia’s Gazprom until now has been the dominant economic partner of the country, which has newly confirmed huge gas reserves. Turkmen gas has been vital for the supply chain of Gazprom and dates back to the era when Turkmenistan was an integral part of the Soviet Union and the Soviet economic infrastructure.
When ’President for Life,’ Saparmurat Niyazov, known as ‘Türkmenbaşy’ or ‘leader of the Turkmens,’ died unexpectedly in December 2006, Washington began entertaining hopes of weaning the new President, Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedow, away from Russia and into the US orbit. To date they have met with little success.
The Medvedev-Berdimuhamedow December agreements included new agreements for Turkmen long-term gas supplies to Gazprom which will fill the South Stream pipeline either directly or by replacing Russian gas to the same -- meaning Nabucco is left out in the cold there.
Nabucco high and dry...
The active pipeline diplomacy of Russia and Gazprom in recent months has dealt a devastating blow to Washington’s favored alternative, Nabucco, which is planned to run from the Caspian region and Middle East via Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary with Austria and further on to Central and Western European gas markets, some 3,300 km, starting at the Georgian-Turkish and/or Iranian-Turkish border. End station would be Baumgarten in Austria. The project is parallel to the existing US-backed Baku-Tbilisi-Erzurum oil pipeline and could transport 20 billion cubic meters of gas a year. Two-thirds of the pipeline would pass through Turkish territory.
 |
| Proposed Nabucco pipeline project: all potential gas suppliers to the US-backed project are in doubt as Moscow outflanks USA |
Today the future of Nabucco is in grave doubt. The problem is that Russia’s Gazprom has all but locked up long-term gas contracts with all the potential suppliers of gas for Nabucco, leaving Nabucco high and dry. Thus, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran and Iraq are being touted as potential suppliers to Nabucco.
Until now the main gas supply for Nabucco should be Azerbaijan, the source of large oil reserves captured by a BP-led Anglo-American consortium bringing Baku oil from the Caspian Sea to the west, independent of Russia. That Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan oil pipeline was a major reason Washington backed the 2004 Georgian ‘Rose Revolution’ that put dictator Mikhail Saakashvili into power.
 |
| Energy rich Azerbaijan prefers to play both sides of Russia/US pipeline game |
 |
| The Shah Deniz platform during transport from the yard in the end of April 2006 |
Currently, even a minimal agreement between Turkey and Azerbaijan for delivery of Azeri gas to Nabucco is in serious doubt. Despite the highly publicized Turkish government decision in 2009 to finally join Nabucco, the vital talks between Turkey and the Azeri government remain stalemated. Despite repeated interventions from US Special Envoy on Eurasian Energy Richard Morningstar to force a final deal, talks remain deadlocked as of this writing. Adding to the woes of Washington’s Nabucco dreams, one of the key partners of the Nabucco, Austria’s OMV, told the Dow Jones wire service at the end of January that the Nabucco pipeline would not be built if demand is too low.
In terms of other options being proposed by some in Washington, for Iraqi gas to flow into Nabucco it would have to go through the Kurdish regions of both Iraq and of Turkey, giving the Kurdish minorities a potential major new revenue source, something not so very welcome in Istanbul. Iran as a potential gas source is at present not in the Washington calculus because of the tensions over Iranian nuclear plans, but more because of Iran’s enormous influence over the future of Iraq, where they exercise significant influence on the majority Shi’ite population there.
Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan, though both have significant natural gas reserves, are even more politically and geographically unlikely as sources of gas for essentially an anti-Russian project. Their distance would mean skyrocketing costs, pricing it far above gas from Gazprom’s South Stream.
In a true exercise of Byzantine diplomacy, Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan invited both Russia and Iran to join the Nabucco project. According to RIA Novosti, Erdogan stated, “We want Iran to join the project when conditions will allow, and also hope for Russia’s participation in it.” Then, just weeks after a formal signing of the Nabucco agreement with the US, during Putin's visit to Ankara in August 2009, Turkey granted Russia's state-run natural-gas monopoly Gazprom use of its territorial waters in the Black Sea, where Moscow wants to route its South Stream pipeline to deliver gas to Eastern and Southern Europe. In exchange, Gazprom agreed to build a pipeline across Turkey from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean.
In early January 2010, the Turkish government furthered its growing ties with Russia during a two day visit to Moscow by Prime Minister Erdogan during which energy and the South Caucasus were discussed. Washington’s Radio Liberty calls it a “new strategic alliance“ between the once-bitter Cold War rivals. Significantly, Turkey is also in NATO.
This is no passing fad. Press in both countries speak openly of a Russo-Turkish “strategic partnership.“ Today Turkey is Russia’s largest market for export of Russian oil and gas combined. As well the two countries are discussing plans for Russia to build Turkey’s first nuclear power plant to meet Turkey’s electricity demand. Bilateral Turkish-Russian trade last year reached $38 billion making Russia Turkey’s largest trade partner. The figure is expected to grow some 300% over the next five years, creating a solid and expanding pro-Russia trade lobby in Turkey. The two countries are in detailed negotiation over some $30 billion in new trade agreements, including Turkey’s nuclear power plant, as well as the South Stream, Blue Stream Turkish-Russian gas pipelines and a Samsun-Ceyhan oil pipeline from Russia to Turkey’s Mediterranean coast.
Indicating how many land mines could explode in the face of Nabucco’s backers, especially in Washington, the Turkish parliament on March 4, 2010 approved a bill on the construction of the Nabucco pipeline. But the same day the US House of Representatives Foreign Affairs Committee passed a non-binding resolution calling the World War I-era killing of Armenians genocide.
The vote led to the immediate recall of Turkey’s Ambassador to Washington as a protest, and will possibly lead to even closer cooperation between Moscow and Ankara on matters of mutual interest, including South Stream.
The vote led to the immediate recall of Turkey’s Ambassador to Washington as a protest, and will possibly lead to even closer cooperation between Moscow and Ankara on matters of mutual interest, including South Stream.
The European Union has just approved a $3 billion general economic stimulus that includes $273 million for Nabucco. At an estimated final cost of $11 billion, that is hardly convincing support for Nabucco. Moreover, the money is being frozen until a final go-ahead for Nabucco is clear, indicating that the countries of the EU are hardly as eager as Washington to back the risky Nabucco counter to Moscow’s South Stream. The EU has said if there is no firm agreement between Nabucco backers and Turkmenistan for gas supply within six months, the money will be used for other projects.
The combination of neutralizing the threat of Ukraine in NATO, starting construction of the strategically important Nord Stream Russian pipeline to Germany and westwards, and Russia advancing its South Stream gas pipeline plans has effectively rendered Washington’s Nabucco pipeline counter-strategy impotent. These developments ensure that Russia’s role as Europe’s largest energy supplier is secure. In recent years Russia has grown to become the source for almost 30% of EU oil imports and by far the largest share of its natural gas. That has enormous strategic geopolitical significance, a point not missed in Washington.
However, with its role in Europe seemingly shored up and the Orange Revolution de facto rolled back, Russia’s policymakers are increasingly turning to the east and the energy demands of its cooperation partner and former Cold War foe, China.
Moscow Goes East
 |
| ESPO pipeline supplies oil to China |
The final link of pipeline to the port of Kozmino is due to be completed in 2014, costing an added $10 billion and resulting in a pipeline almost 4800 kilometers long, a distance greater than from Los Angeles to New York. Moscow and Beijing have also agreed to build a spur pipeline from Skovorodino to Daqing in China’s Heilongjiang province in northeastern China, the center of its energy and petrochemical industry and site of China’s largest oilfield. When completed, the pipeline will carry eastward an annual 80 mm tons of oil from Siberia, including 15 mm tons to China through an additional spur.
An indication of the priority that energy-hungry China places on Russian oil, China has loaned $25 billion to Russia in exchange for oil deliveries over the next two decades. In February 2009, when world oil prices dropped to $25 a barrel from a record high $147 some six months before, Russian oil giant Rosneft and pipeline operator Transneft were on the brink of collapse. Beijing, in a deft and swift move to insure future oil from Russia’s East Siberia fields, stepped in and through the state-owned Chinese Development Bank offered loans to Rosneft and Transneft of $10 billion and $15 billion respectively, a $25 billion dollar investment to accelerate the construction of the pacific pipeline. For its part, Russia agreed to develop further new fields, build the ESPO leg for Daqing from Skorovodino to the Chinese border, a distance of some 43 miles, and supply China with at least 300,000 barrels of highly in-demand sweet or low sulfur crude oil per day.
Beyond the Russian border, in the Chinese interior, Beijing will construct a domestic pipeline approximately 600 miles long to Daqing. The Chinese loan was made at 6% interest and would require Russian oil be sold to China for $22 per barrel. Today the average international oil price has recovered to some $80 a barrel, meaning China has locked in a golden prize. Rather than renege on the price deal, Moscow has clearly decided the strategic advantages of the China link outweigh possible revenue loss. It retains price control over the rest of the oil flowing through the ESPO pipeline on to the Pacific for other Asian markets.
Beyond the Russian border, in the Chinese interior, Beijing will construct a domestic pipeline approximately 600 miles long to Daqing. The Chinese loan was made at 6% interest and would require Russian oil be sold to China for $22 per barrel. Today the average international oil price has recovered to some $80 a barrel, meaning China has locked in a golden prize. Rather than renege on the price deal, Moscow has clearly decided the strategic advantages of the China link outweigh possible revenue loss. It retains price control over the rest of the oil flowing through the ESPO pipeline on to the Pacific for other Asian markets.
Whereas the energy markets of Western Europe pose a relatively stagnant demand prospect, those of China and Asia are booming. Moscow is making a major shift eastwards in light of that fact. At the end of 2009, the Russian government released a comprehensive energy report entitled “Energy Blueprint for 2030.” It calls for substantial domestic investment in the East Siberian fields, and speaks of a shift in oil exports toward Northeast Asia, with the share of the Asia Pacific region in Russian exports growing from 8% in 2008 to 25% over the next years. That will have significant political consequences for both Russia and Asia, especially China.
China passed Japan several years ago to become the world’s second major oil importing nation after the United States. The issue of Chinese energy security is of such paramount importance for China that Prime Minister Wen Jaibao has just been named to head a cross-ministry National Energy Council to coordinate all issues of China’s energy policy.
Russian begins LNG deliveries for Asia
A few months before the completion of the ESPO oil pipeline to the Pacific, Russia began its first ever deliveries of Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) from the Gazprom-led Sakhalin-II project, a joint venture that includes Japan’s Mitsui and Mitsubishi as well as the Anglo-Dutch Shell. For Russia the project will give her invaluable experience in the rapidly expanding global LNG market, a market not dependent on fixed long-term pipeline construction.
 |
| The Grand Elena is one of two LNG carriers constructed for the Sakhalin II project. |
 |
| Central Asia-China Gas Pipeline |
It marked the first pipeline to bring Central Asian natural gas to China. The pipeline from Turkmenistan will be connected to a branch line from western Kazakhstan, scheduled to open in 2011 and which will supply natural gas from several Kazakh fields to Alashankou in China’s Xinjiang Province. Little wonder that Chinese authorities were none too pleased with ethnic Uighur riots in July of 2009, which the Chinese government claimed was instigated by the Washington-based World Uyghur Congress (WUC) and its leader Rebiya Kadeer, who reportedly has close ties to the US Congress’ regime-change NGO, the National Endowment for Democracy. Xinjiang is becoming ever more strategically important to future Chinese energy flows.
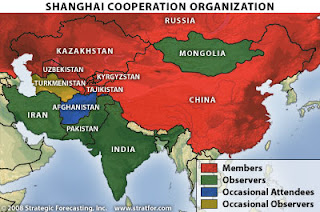
Far from a threat to Russia’s energy strategy as some western commentators claim, the Turkmen-China gas pipeline in effect serves to deepen the economic ties within the countries of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, SCO, at the same time it locks up for China a major portion of Turkmen gas that might have gone to the floundering Nabucco pipeline favored by Washington. That can only be to the geopolitical advantage of Russia which would lose a major economic influence were Nabucco to succeed.
The SCO, founded in 2001 in Shanghai by the heads of state of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, has evolved into what might be called Halford Mackinder’s worst nightmare—a vehicle for welding close economic and political cooperation of the key Eurasian land powers independently of the United States. In his widely-publicized 1997 book, The Grand Chessboard, former US National Security Adviser Zbigniew Brzezinski bluntly stated, “It is imperative that no Eurasian challenger emerges capable of dominating Eurasia and thus of also challenging America. The formulation of a comprehensive and integrated Eurasian geostrategy is therefore the purpose of this book.” He added the warning, “Henceforth, the United States may have to determine how to cope with regional coalitions that seek to push America out of Eurasia, thereby threatening America's status as a global power.” In the wake of the events of September 2001, events which many Russian intelligence experts doubted to be the work of a rag-tag band of Muslim Al Qaeda fanatics, the SCO has begun to take the character of the very threat that Brzezinski, a student of Mackinder, warned of. In a recent interview on The Real News, Brzezinski also bemoaned the lack of any coherent Eurasian strategy, notably in Afghanistan and Pakistan, on the part of the Obama Administration.
Russia also moves North to the Arctic Circle
Completing Russia’s new geopolitical energy strategy, the remaining move is to the north, in the direction above the Arctic Circle.
In August 2007, then-Russian President Vladimir Putin caught the notice of NATO and Washington when he announced that two Russian submarines had symbolically planted the Russian flag at a depth of over 4 kilometers on the Arctic Ocean floor, laying claim to the seabed resources. Then in March 2009 Russia announced that it would establish military bases along the northern coastline. New US NATO Supreme Commander Admiral James Stavridis expressed concern that Russian presence in the Arctic could pose serious problems for NATO.
In April 2009, the state-owned Russian news service RIA Novosti reported that the Russian Security Council had published an official policy paper on its Web site titled, "The fundamentals of Russian state policy in the Arctic up to 2020 and beyond." The paper described the principles guiding Russian policy in the arctic, saying it would involve establishing significant Russian army, border and coastal guard forces there "to guarantee Russia's military security in diverse military and political circumstances," according to the report.
In addition to staking claim to some of the world’s largest untapped oil and gas resources, Russia is clearly moving to pre-empt a further US expansion of its misleadingly named missile ‘defense’ to the Arctic Circle in echoes of the old Cold War era. Last September Dmitry Rogozin, Russia's envoy to NATO, told Vesti 24 television channel that the Northern Sea Route through the Arctic might provide the United States with an effective theater to position shipboard missile defenses to counter Russian weapons. His remarks followed the announcement by US President Barack Obama that the US would place such defenses on cruisers as a more technically advanced alternative.
A 2008 estimate by the US Government’s US Geological Survey (USGS) concluded that the area north of the Arctic Circle contains staggeringly large volumes of oil and natural gas. They estimated that more than 70% of the region’s undiscovered oil resources occur in five provinces: Arctic Alaska, Amerasia Basin, East Greenland Rift Basins, East Barents Basins, and West Greenland-East Canada. More than 70% of the undiscovered natural gas is believed located in three provinces, the West Siberian Basin, the East Barents Basins, and Arctic Alaska. Some 84% of the undiscovered oil and gas occurs offshore. The total undiscovered conventional oil and gas resources of the Arctic are estimated to be approximately 90 billion barrels of oil, 1,669 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, and 44 billion barrels of natural gas liquids. The main potential beneficiary is likely to be Russia that has the largest share of territory in the region.
Contrary to widely held beliefs in the west, the Cold War did not end with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 or the fall of the Berlin Wall in November 1989, at least not for Washington. Seeing the opportunity to expand the reach of US military and political power, the Pentagon began a systematic modernization of its nuclear arsenal and a step-wise extension of NATO membership right to the doorstep of Moscow, something that then-Secretary of State James Baker III had pledged to Russian President Mikhail Gorbachev would not happen. Washington lied. During the chaos of the Yeltsin years, Russia’s economy collapsed under IMF-mandated ‘shock therapy’ and systematic looting by western companies in cahoots with a handful of newly created Russian oligarchs.
The re-emergence of Russia as a factor in world politics, however weakened from the economic shocks of the past two decades, has been based on a strategy that obviously has drawn from principles of asymetric warfare, economic as well as military. Russia’s present military preparedness is no match for the awesome Pentagon power projection. However, she still maintains the only nuclear strike force on the planet that is capable of posing a mortal threat to the military power of the Pentagon. In cooperation with China and its other Eurasian SCO partners, Russia is clearly using its energy as a geopolitical lever of the first order.
The recent events in Ukraine and the rollback there of the ill-fated Washington Orange Revolution, in the context now of Moscow’s comprehensive energy politics, present Washington strategists with a grave challenge to their assumed global “Full Spectrum” dominance. The US debacle in Afghanistan and the uneasy state of affairs in US-occupied Iraq have done far more than any Russian military challenge to undermine the global influence of the United States as sole decision maker of a ‘unipolar world.’
Notes
1 Press Trust of India, 2009: Ukraine Becomes World's Third Largest Grain Exporter, accessed in
http://blog.kievukraine.info/2009_12_01_archive.html.
2 Stepan P. Poznyak, Ukrainian Chornozem: past, Present, Future, paper of 18th World Congress of Soil Science, July 9-15, 2006, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, accessed in
http://www.ldd.go.th/18wcss/techprogram/P12419.HTM
3 The American Chamber of Commerce in Ukraine, Chamber Members, accessed in http://www.chamber.ua/
4 KosivArt, Ukraine Natural Resources, accessed in http://www.kosivart.com/eng/index.cfm/do/ukraine.natural-resources
5 Halford J. Mackinder, Democratic Ideals and Reality, 1919, reprint 1942, Henry Holt and Company, New York, p. 150.
6 F. William Engdahl, Ukraine and Georgia: Entry into NATO Put Off Indefinitely, December 4, 2008, in http://www.globalresearch.ca/index.php?context=va&aid=11277
7 John Arquilla, David Ronfeldt, Swarming and the Future of Conflict, Santa Monica: RAND, 2000.
8 US Department of State, John E. Herbst Biography, accessed in http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/biog/67065.htm.
9 Michel Chossudovsky, IMF Sponsored "Democracy" in The Ukraine, 28 November 2004, accessed in http://globalresearch.ca/articles/CHO411D.html
10 Kateryna Yushchenko, Biography, on My Ukraine: Personal Website of Viktor Yushchenko, 31 March 2005, accessed in http://www.yuschenko.com.ua/eng/Private/Family/2822/.
11 Wikipedia, Orange Revolution, accessed in http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orange_Revolution.
12 Andrew Osborn, We Treated Poisoned Yushchenko, Admit Americans, The Independent U.K., March 12, 2005, accessed in http://www.truthout.org/article/us-played-big-role-ukraines-orange-revolution.
13 Dmitry Sudakov, USA Assigns $20 million for Elections in Ukraine, Moldova, Pravda.ru, 11 March 2005.
14 ‘Nicholas,’ Forces Behind the Orange Revolution, Kiev Ukraine News Blog , January 10, 2005 accessed in http://blog.kievukraine.info/2005/01/forces-behind-orange-revolution.html.
15 Jim Nichol et al, Russia’s Cutoff of Natural Gas to Ukraine: Context and Implications, US Congressional Research Service Report for Congress, Washington, D. C. February 15, 2006.
16 Yuras Karmanau, Half-empty chamber greets Ukraine's new president, Associated Press, February 25, 2010, accessed in http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20100225/ap_on_re_eu/eu_ukraine_president
17 Inform: Bloc of Yulia Tymoshenko Release # 134, EPP Throws Weight Behind Tymoshenko, 16
December, 2009, accessed in http://www.ibyut.com/index_files/792.html
18 Stefan Wagstyl and Roman Oleachyk, Ukraine Election Divides Oligarchs, London Financial Times, January 15, 2010.
19 TraCCC, Pavlo Lazarenko: Is the Former Ukrainian Prime Minister a Political Refugee or a Financial Criminal?, Organized Crime and Corruption Watch, Vol. 2, No. 2, Summer 2000, Washington D.C., American University Transnational Crime and Corruption Center.
20 Ian Traynor, Ukrainian Leader Appoints Billionaire as his PM, The Guardian, 24 January, 2005.
21 United States Embassy in Minsk, US Government Assistance FY 97 Annual Report, United States Embassy in Minsk, Belarus, 1998, http://belarus.usembassy.gov/assistance1997.html
22 Eurogas (European Union of the Natural Gas Industry), Natural Gas Demand and Supply: Long-Term Outlook to 2030, Brussels, Belgium, 2007, accessed in www.euro gas .org/.../Euro gas %20long%20term%20outlook%20to%202030%20-%20fina...
23 Jim Nichol, op. cit.
24 US Department of Energy, Ukraine Country Analysis Brief, Energy Information Administration, August 2007, Washington DC, accessed in http://www.eia.doe.gov/cabs/Ukraine/Full.html
25 International Energy, Russia to supply 116 bn cm of gas to Europe via Ukraine in 2010, Beijing,
November 19, 2009, accessed in http://en.in-en.com
26 Simon Taylor, Why Russia's Nord Stream is winning the pipeline race, January 29, 2009, EuropeanVoice.com, accessed in http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/imported/why-russia
%E2%80%99s-nord-stream-is-winning-the-pipeline-race/63780.aspx
27 RAI Novosti, Russia pledges 30-40% discount on gas for Belarus in 2010, November 23, 2009,
accessed in http://en.rian.ru
28 UPI, Nord Stream to supply UK by 2012, December 1, 2009, accessed in http://www.upi.com
29 Gazprom, Major Projects: South Stream, accessed in http://old.gazprom.ru/eng/articles/article27150.shtml
30 Trend, Bulgaria ready to participate in both South Stream and Nabucco, Baku, Azerbaijan, December 5, 2009, accessed in http://en.trend.az
31 Olja Stanic, Bosnian Serbs to join Russia-led gas pipeline, Reuters, March 5, 2005, Banka Luka Bosnia, accessed in http://in.reuters.com/article/oilRpt/idINLDE6241B920100305
32 For more on this fascinating and all-but-forgotten history of the German-British imperial rivalries over the Berlin-Baghdad Railway project in the prelude to the First World War, see, F. William Engdahl, A Century of War: Anglo-American Oil Politics and the New World Order, London, Pluto Press, 2004, pp. 22-28.
33 Mahir Zeynalov, Azerbaijan-Gazprom agreement puts Nabucco in jeopardy, Today’s Zaman, July 16, 2009, accessed in http://www.todayszaman.com/tz-web/sabit.do?sf=aboutus
34 Saban Kardas, Delays in Turkish-Azeri Gas Deal Raises Uncertainty Over Nabucco, Eurasia Daily
Monitor, Vol. 7 Issue 39, February 26, 2010.
35 Ibid.
36 Brian Whitmore, Moscow Visit by Turkish PM Underscores New Strategic Alliance, Radio Liberty/Radio Free Europe, January 13, 2010, accessed in http://www.rferl.org/content/Moscow_Visit_By_Turkish_PM_Underscores_New_Strategic_Alliance/1927504.html
37 Ibid.
38 Faruk Akkan, Turkey and Russia move closer to building strategic partnership, RAI Novosti, January 15, 2010, accessed in http://en.rian.ru/valdai_foreign_media/20100115/157554880.html
39 RAI Novosti, Russian delegation to discuss Turkey nuclear power plant plan, Ankara, February 18, 2010, accessed in http://en.rian.ru/world/20100218/157927131.html
40 Kommersant, Nabucco's future depends on Turkmenistan, Moscow, March 9, 2010, accessed in
http://en.rian.ru/papers/20100309/158135872.html
41 US Energy Information Administration, Russia: Oil Exports, accessed in http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/cabs/Russia/Oil_exports.html
42 Greg Shtraks, The Start of a Beautiful Friendship? Russia begins exporting oil through the Pacific port of Kozmino, Jamestown Foundation Blog, Washington D.C., December 11, 2009, accessed in http://jamestownfoundation.blogspot.com/2009/12/start-of-beautiful-friendship-russia.html
43 Ibid.
44 Moscow Times, Putin Launches Pacific Oil Terminal, December 29, 2009, accessed in
http://www.themoscowtimes.com
45 Zhang Guobao, Chinese Energy Sector Turns Crisis into Opportunities, January 28, 2010, accessed in www.chinadaily.com.cn
46 Isabel Gorst, Geoff Dyer, Pipeline brings Asian gas to China, London, Financial Times, December 14, 2009.
47 Reuters, China calls Xinjiang riot a plot against its rule, 5 July 2009, accessed in
http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE56500R20090706
48 Zbigniew Brzezinski, The Grand Chessboard: American Primacy and It's Geostrategic Imperatives, New York, Basic Books, 1998 (paperback), p. xiv.
49 Ibid., p.55.
50 UPI.com, Russia’s Arctic Circle Claims Worry NATO, October 2, 2009, accessed in
http://www.upi.com/Top_News/2009/10/02/Russias-Arctic-Circle-claims-worry-NATO/UPI-55371254525955/
51 Mark Sieff, Russia creating new armed forces to boost power in arctic, UPI.com, April 6, 2009, accessed in http://www.upi.com/Business_News/Security-Industry/2009/04/06/Russia-creating-new-armedforces-to-boost-power-in-arctic/UPI-88341239045539/
52 UPI.com, Russia fears missile defenses in Arctic, September 29, 2009, accessed in
http://www.upi.com/Top_News/2009/09/29/Russia-fears-missile-defenses-in-Arctic/UPI-80901254231286/
53 Donald L. Gautier, et al, USGS Arctic Oil and Gas Report: Estimates of Undiscovered Oil and Gas North of the Arctic Circle, Washington D.C., USGS, July 2008, accessed in http://geology.com/usgs/arctic-oiland-gas-report.shtml
54 F. William Engdahl, Full Spectrum Dominance: Totalitarian Democracy in the New World Order,
Wiesbaden, edition.engdahl, October 2009, p.3.
http://blog.kievukraine.info/2009_12_01_archive.html.
2 Stepan P. Poznyak, Ukrainian Chornozem: past, Present, Future, paper of 18th World Congress of Soil Science, July 9-15, 2006, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, accessed in
http://www.ldd.go.th/18wcss/techprogram/P12419.HTM
3 The American Chamber of Commerce in Ukraine, Chamber Members, accessed in http://www.chamber.ua/
4 KosivArt, Ukraine Natural Resources, accessed in http://www.kosivart.com/eng/index.cfm/do/ukraine.natural-resources
5 Halford J. Mackinder, Democratic Ideals and Reality, 1919, reprint 1942, Henry Holt and Company, New York, p. 150.
6 F. William Engdahl, Ukraine and Georgia: Entry into NATO Put Off Indefinitely, December 4, 2008, in http://www.globalresearch.ca/index.php?context=va&aid=11277
7 John Arquilla, David Ronfeldt, Swarming and the Future of Conflict, Santa Monica: RAND, 2000.
8 US Department of State, John E. Herbst Biography, accessed in http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/biog/67065.htm.
9 Michel Chossudovsky, IMF Sponsored "Democracy" in The Ukraine, 28 November 2004, accessed in http://globalresearch.ca/articles/CHO411D.html
10 Kateryna Yushchenko, Biography, on My Ukraine: Personal Website of Viktor Yushchenko, 31 March 2005, accessed in http://www.yuschenko.com.ua/eng/Private/Family/2822/.
11 Wikipedia, Orange Revolution, accessed in http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orange_Revolution.
12 Andrew Osborn, We Treated Poisoned Yushchenko, Admit Americans, The Independent U.K., March 12, 2005, accessed in http://www.truthout.org/article/us-played-big-role-ukraines-orange-revolution.
13 Dmitry Sudakov, USA Assigns $20 million for Elections in Ukraine, Moldova, Pravda.ru, 11 March 2005.
14 ‘Nicholas,’ Forces Behind the Orange Revolution, Kiev Ukraine News Blog , January 10, 2005 accessed in http://blog.kievukraine.info/2005/01/forces-behind-orange-revolution.html.
15 Jim Nichol et al, Russia’s Cutoff of Natural Gas to Ukraine: Context and Implications, US Congressional Research Service Report for Congress, Washington, D. C. February 15, 2006.
16 Yuras Karmanau, Half-empty chamber greets Ukraine's new president, Associated Press, February 25, 2010, accessed in http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20100225/ap_on_re_eu/eu_ukraine_president
17 Inform: Bloc of Yulia Tymoshenko Release # 134, EPP Throws Weight Behind Tymoshenko, 16
December, 2009, accessed in http://www.ibyut.com/index_files/792.html
18 Stefan Wagstyl and Roman Oleachyk, Ukraine Election Divides Oligarchs, London Financial Times, January 15, 2010.
19 TraCCC, Pavlo Lazarenko: Is the Former Ukrainian Prime Minister a Political Refugee or a Financial Criminal?, Organized Crime and Corruption Watch, Vol. 2, No. 2, Summer 2000, Washington D.C., American University Transnational Crime and Corruption Center.
20 Ian Traynor, Ukrainian Leader Appoints Billionaire as his PM, The Guardian, 24 January, 2005.
21 United States Embassy in Minsk, US Government Assistance FY 97 Annual Report, United States Embassy in Minsk, Belarus, 1998, http://belarus.usembassy.gov/assistance1997.html
22 Eurogas (European Union of the Natural Gas Industry), Natural Gas Demand and Supply: Long-Term Outlook to 2030, Brussels, Belgium, 2007, accessed in www.euro gas .org/.../Euro gas %20long%20term%20outlook%20to%202030%20-%20fina...
23 Jim Nichol, op. cit.
24 US Department of Energy, Ukraine Country Analysis Brief, Energy Information Administration, August 2007, Washington DC, accessed in http://www.eia.doe.gov/cabs/Ukraine/Full.html
25 International Energy, Russia to supply 116 bn cm of gas to Europe via Ukraine in 2010, Beijing,
November 19, 2009, accessed in http://en.in-en.com
26 Simon Taylor, Why Russia's Nord Stream is winning the pipeline race, January 29, 2009, EuropeanVoice.com, accessed in http://www.europeanvoice.com/article/imported/why-russia
%E2%80%99s-nord-stream-is-winning-the-pipeline-race/63780.aspx
27 RAI Novosti, Russia pledges 30-40% discount on gas for Belarus in 2010, November 23, 2009,
accessed in http://en.rian.ru
28 UPI, Nord Stream to supply UK by 2012, December 1, 2009, accessed in http://www.upi.com
29 Gazprom, Major Projects: South Stream, accessed in http://old.gazprom.ru/eng/articles/article27150.shtml
30 Trend, Bulgaria ready to participate in both South Stream and Nabucco, Baku, Azerbaijan, December 5, 2009, accessed in http://en.trend.az
31 Olja Stanic, Bosnian Serbs to join Russia-led gas pipeline, Reuters, March 5, 2005, Banka Luka Bosnia, accessed in http://in.reuters.com/article/oilRpt/idINLDE6241B920100305
32 For more on this fascinating and all-but-forgotten history of the German-British imperial rivalries over the Berlin-Baghdad Railway project in the prelude to the First World War, see, F. William Engdahl, A Century of War: Anglo-American Oil Politics and the New World Order, London, Pluto Press, 2004, pp. 22-28.
33 Mahir Zeynalov, Azerbaijan-Gazprom agreement puts Nabucco in jeopardy, Today’s Zaman, July 16, 2009, accessed in http://www.todayszaman.com/tz-web/sabit.do?sf=aboutus
34 Saban Kardas, Delays in Turkish-Azeri Gas Deal Raises Uncertainty Over Nabucco, Eurasia Daily
Monitor, Vol. 7 Issue 39, February 26, 2010.
35 Ibid.
36 Brian Whitmore, Moscow Visit by Turkish PM Underscores New Strategic Alliance, Radio Liberty/Radio Free Europe, January 13, 2010, accessed in http://www.rferl.org/content/Moscow_Visit_By_Turkish_PM_Underscores_New_Strategic_Alliance/1927504.html
37 Ibid.
38 Faruk Akkan, Turkey and Russia move closer to building strategic partnership, RAI Novosti, January 15, 2010, accessed in http://en.rian.ru/valdai_foreign_media/20100115/157554880.html
39 RAI Novosti, Russian delegation to discuss Turkey nuclear power plant plan, Ankara, February 18, 2010, accessed in http://en.rian.ru/world/20100218/157927131.html
40 Kommersant, Nabucco's future depends on Turkmenistan, Moscow, March 9, 2010, accessed in
http://en.rian.ru/papers/20100309/158135872.html
41 US Energy Information Administration, Russia: Oil Exports, accessed in http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/cabs/Russia/Oil_exports.html
42 Greg Shtraks, The Start of a Beautiful Friendship? Russia begins exporting oil through the Pacific port of Kozmino, Jamestown Foundation Blog, Washington D.C., December 11, 2009, accessed in http://jamestownfoundation.blogspot.com/2009/12/start-of-beautiful-friendship-russia.html
43 Ibid.
44 Moscow Times, Putin Launches Pacific Oil Terminal, December 29, 2009, accessed in
http://www.themoscowtimes.com
45 Zhang Guobao, Chinese Energy Sector Turns Crisis into Opportunities, January 28, 2010, accessed in www.chinadaily.com.cn
46 Isabel Gorst, Geoff Dyer, Pipeline brings Asian gas to China, London, Financial Times, December 14, 2009.
47 Reuters, China calls Xinjiang riot a plot against its rule, 5 July 2009, accessed in
http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE56500R20090706
48 Zbigniew Brzezinski, The Grand Chessboard: American Primacy and It's Geostrategic Imperatives, New York, Basic Books, 1998 (paperback), p. xiv.
49 Ibid., p.55.
50 UPI.com, Russia’s Arctic Circle Claims Worry NATO, October 2, 2009, accessed in
http://www.upi.com/Top_News/2009/10/02/Russias-Arctic-Circle-claims-worry-NATO/UPI-55371254525955/
51 Mark Sieff, Russia creating new armed forces to boost power in arctic, UPI.com, April 6, 2009, accessed in http://www.upi.com/Business_News/Security-Industry/2009/04/06/Russia-creating-new-armedforces-to-boost-power-in-arctic/UPI-88341239045539/
52 UPI.com, Russia fears missile defenses in Arctic, September 29, 2009, accessed in
http://www.upi.com/Top_News/2009/09/29/Russia-fears-missile-defenses-in-Arctic/UPI-80901254231286/
53 Donald L. Gautier, et al, USGS Arctic Oil and Gas Report: Estimates of Undiscovered Oil and Gas North of the Arctic Circle, Washington D.C., USGS, July 2008, accessed in http://geology.com/usgs/arctic-oiland-gas-report.shtml
54 F. William Engdahl, Full Spectrum Dominance: Totalitarian Democracy in the New World Order,
Wiesbaden, edition.engdahl, October 2009, p.3.